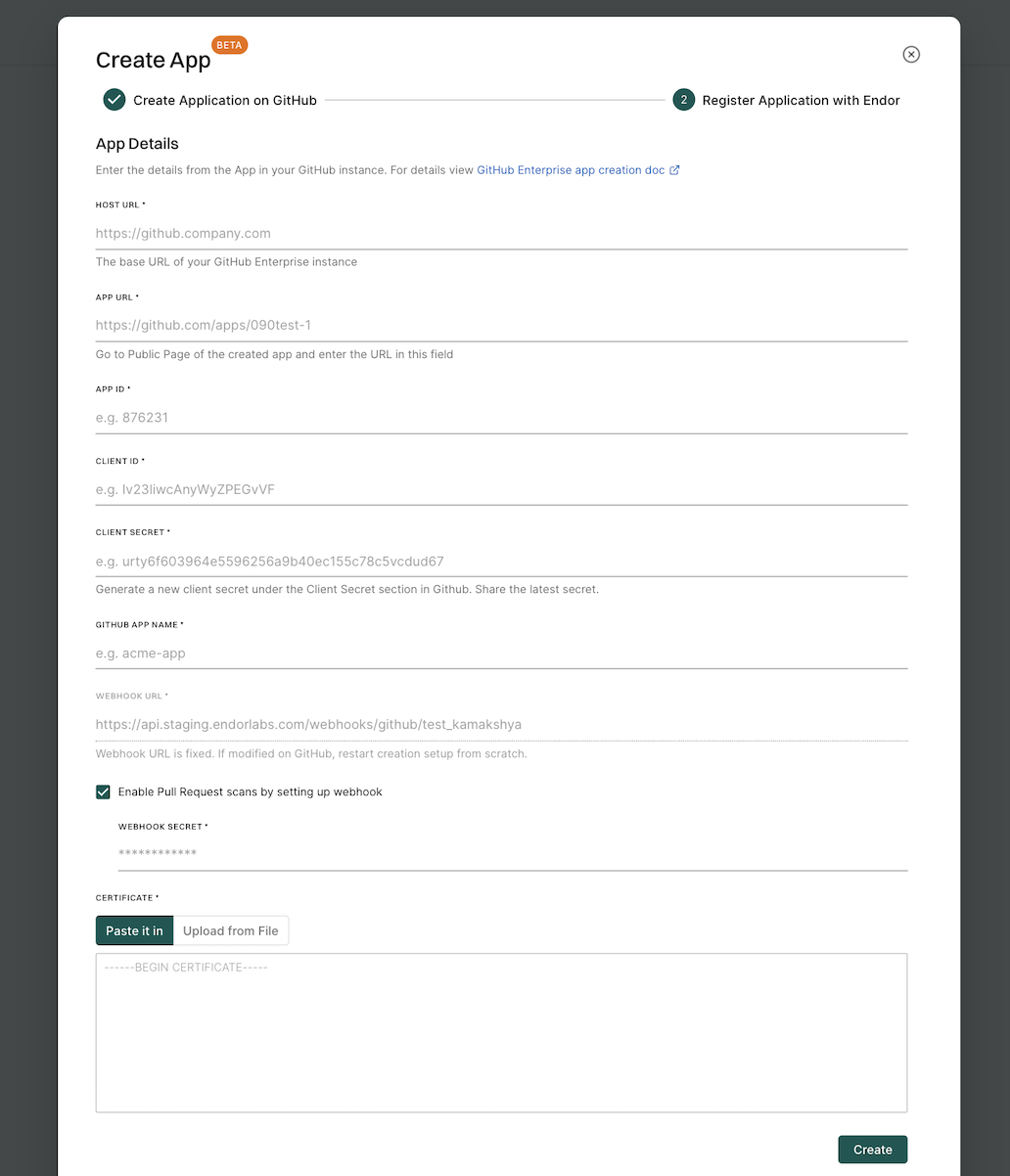
With the Endor Labs GitHub App or the Endor Labs GitHub Enterprise Server App you can enhance the security of your repository through the following types of scans.
Scan complete repository
The Endor Labs App automatically scans your repositories every 24 hours for potential security issues and operational risks, providing up-to-date information about your projects’ security posture.
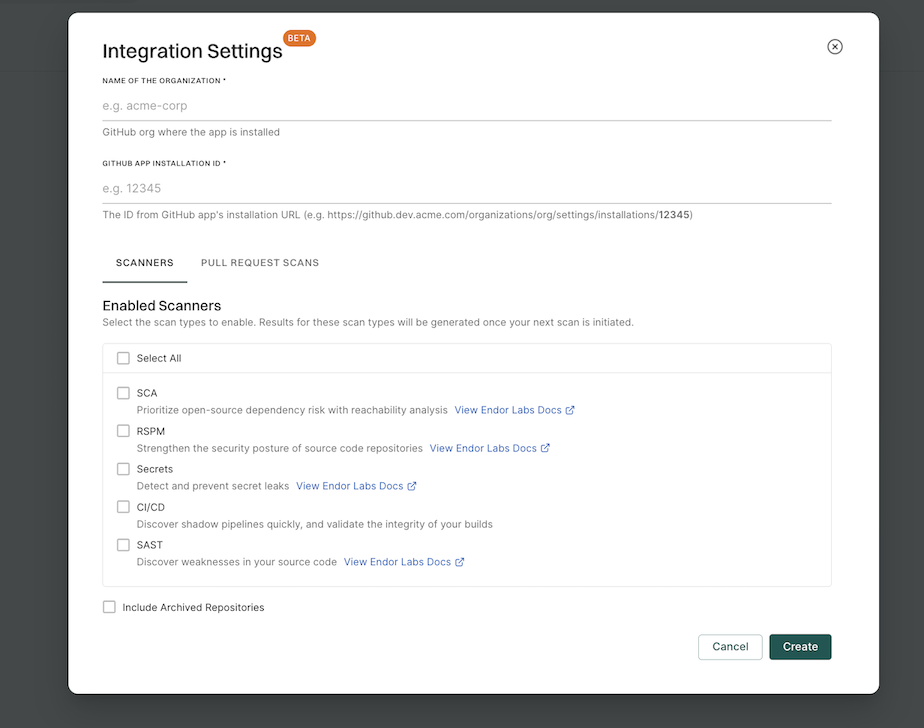
- You can use the GitHub App to selectively scan your repositories for Software Composition Analysis (SCA), secrets, Repository Security Posture Management (RSPM), or GitHub Actions.
- While the automated scan happens every 24 hours, you can manually trigger a rescan outside this schedule from the Endor Labs user interface. See Rescan projects.
- After each scan, the GitHub App reports any new findings or changes to release versions of your code. Review the scan results from the Endor Labs user interface.
Scan pull requests
After scanning the complete repository, it’s important to address the pull requests submitted by users. Administrators can enable a fully automated scanning process for all pull requests and merges initiated into the main branch.
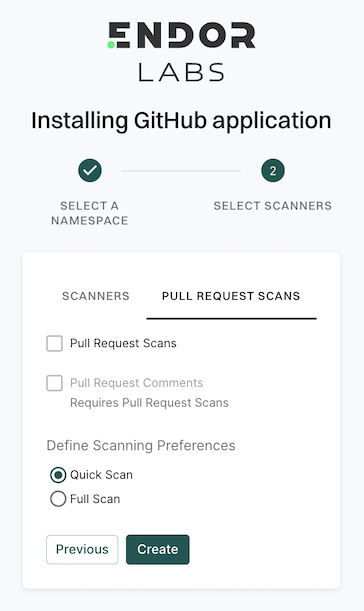
To automatically scan the PRs, set the pull request preferences during the GitHub App installation or edit the integration preferences afterward. For GitHub Enterprise Server App, set the preferences during installation or edit the integration preferences afterward.
Whenever a PR is created against a repository, the Endor Labs GitHub App performs an incremental scan to detect any changes in resolved dependencies that may introduce new vulnerabilities. These incremental scans are CI runs and are not monitored. You can see the results of the scan on GitHub.
Based on your preferences, it performs a quick scan or a full scan before merging the PRs into the main branch.
- Quick Scan performs dependency resolution but does not conduct reachability analysis to prioritize vulnerabilities. The quick scan enables users to swiftly identify potential vulnerabilities in dependencies, ensuring a smoother and more secure merge into the main branch.
- Full Scan performs dependency resolution, reachability analysis, and generate call graphs for supported languages and ecosystems. This scan enables users to get complete visibility and identifies all issues related to dependencies and call graph generation, before merging into the main branch. Full scans may take longer to complete, potentially delaying PR merges.
Pull request comments
Pull request comments are automated comments added to pull requests when Endor Labs detects policy violations or security issues during scans. When a PR is raised or updated, Endor Labs runs scans on the proposed changes and adds a comment if any violations are detected based on the configured action policies.
You can enable PR comments during the initial setup of the GitHub App or GitHub App (Pro), or by editing an existing integration. Once enabled, Endor Labs automatically adds comments to pull requests when policy violations are detected after you configure an action policy. See Configure Action policy for PR comments for more information.
Types of PR comments
Configure Action policy for PR comments
You must create an Action policy to receive comments on your pull request after enabling PR comments.
- Create an Action policy.
- Set the Branch Type to
Pull Requestso the policy applies specifically to pull request scans. - Under Action, select Enforce Policy, then choose:
- Warn to post a comment without breaking the build.
- Break the Build to fail the build and block the pull request.
- Define the scope of the policy using tags. Only projects that match the specified tags will receive PR comments.
Customize PR comments templates
Endor Labs provides a default template with standard information that will be included in your pull requests as comments. You can use the default template, or you can choose to edit and customize this template to fit your organization’s specific requirements. You can also create custom templates using Go Templates.
- Select Manage > Integrations from the left sidebar.
- Click Edit Template next to GitHub PR comments under Notifications.
- Make the required changes and click Save Template.
PR comments data model
To create custom templates for PR comments, you must understand the data supplied to the template.
See the following protobuf specification for the GithubCommentData message that this template uses.
syntax = "proto3";
package internal.endor.ai.endor.v1;
import "google/protobuf/wrappers.proto";
import "protoc-gen-openapiv2/options/annotations.proto";
import "spec/internal/endor/v1/common.proto";
import "spec/internal/endor/v1/finding.proto";
import "spec/internal/endor/v1/package_version.proto";
import "spec/internal/endor/v1/security_review_pull_request.proto";
option go_package = "github.com/endorlabs/monorepo/src/golang/spec/internal.endor.ai/endor/v1";
option java_package = "ai.endor.internal.spec";
// The list of finding UUIDs.
message FindingUuids {
repeated string uuids = 1;
}
// The map of dependency name to findings.
message DependencyToFindings {
map<string, FindingUuids> dependency_to_findings = 1;
}
// The map of PackageVersion UUID to DependencyToFindings.
message PackageToDependencies {
map<string, DependencyToFindings> package_to_dependencies = 1;
}
message GithubCommentData {
// The header of the PR comment. Identifies the PR comment published by Endor Labs.
// It should always be at top of the template.
google.protobuf.StringValue comment_header = 1;
// The footer of the PR comment.
google.protobuf.StringValue comment_footer = 2;
// The map of finding UUID to finding object.
map<string, internal.endor.ai.endor.v1.Finding> findings_map = 3;
// The map of policy UUID to policy name.
// This will contain only the policies that are triggered or violated.
map<string, string> policies_map = 4;
// The map of policy UUID to the list of finding UUIDs.
map<string, FindingUuids> policy_findings_map = 5;
// The map of PackageVersion UUID to PackageVersion object.
map<string, internal.endor.ai.endor.v1.PackageVersion> package_versions_map = 6;
// The data needs to be grouped as follows:
//
// - Policy 1
// - Package 1
// - Dependency Package 1
// - Finding 1
// - Finding 2
// - Dependency Package 2
// - Finding 3
// - Finding 4
// - Package 2
// - Dependency Package 1
// - Finding 1
// - Finding 5
// - Policy 2
// ....
//
// Map 0[PolicyUUID]/Map 1[PkgVerUUID]/Map 2 [Dep Names]/Finding UUID
map<string, PackageToDependencies> data_map = 7;
google.protobuf.StringValue api_endpoint = 8;
}
// Data structure for security review comments on pull requests.
message SecurityReviewCommentData {
option (internal.endor.ai.endor.v1.parent_kinds) = {};
option (grpc.gateway.protoc_gen_openapiv2.options.openapiv2_schema) = {
json_schema: {
extensions: {
key: "x-internal";
value {bool_value: true}
}
}
};
// Represents a specific security risk identified in the code review.
message SecurityRisk {
// Icon representing the severity level of the risk.
google.protobuf.StringValue severity_icon = 1;
// The category or type of the security risk.
google.protobuf.StringValue category = 2;
// The title or name of the security risk.
google.protobuf.StringValue title = 3;
// Link to the specific code location where the risk was identified.
google.protobuf.StringValue code_link = 4;
// Detailed description of the security risk and potential impact.
google.protobuf.StringValue description = 5;
// The level of the security risk.
google.protobuf.StringValue level = 6;
// The type of impact (improvement or regression).
google.protobuf.StringValue impact_type = 7;
}
// Represents an issue that occurred during the security analysis.
message AnalysisIssue {
// The type of the issue.
SecurityReviewPullRequest.Spec.IssueType type = 1;
// A descriptive message about the issue.
google.protobuf.StringValue message = 2;
// List of error messages encountered during analysis.
repeated string errors = 3;
// List of files that were skipped during analysis.
repeated string skipped_files = 4;
// List of files that were summarized instead of fully analyzed.
repeated string summarized_files = 5;
}
// The header of the security review comment.
// It should always be at the top of the template.
google.protobuf.StringValue comment_header = 1;
// The footer of the security review comment.
google.protobuf.StringValue comment_footer = 2;
// A description of the changes made in the pull request.
google.protobuf.StringValue changes_description = 3;
// A general security assessment description.
google.protobuf.StringValue security_description = 4;
// The list of identified security risks in the pull request.
repeated SecurityRisk security_risks = 5;
// The list of issues encountered during analysis.
repeated AnalysisIssue analysis_issues = 6;
}
See the following sections to understand the Finding and PackageVersion definitions that are used in this protobuf specification:
See the following specification to understand the additional functions that are also available. You can access these functions by using their corresponding keys.
// FuncMap contains the additional functions that are available to CommentTemplate.
var FuncMap = template.FuncMap{
"now": utils.ToTime, // 'now' gives the current time
// 'enumToString' coverts the enums for finding level, finding category and finding tags to string
"enumToString": utils.EnumToString,
// 'getPackageVersionURL' returns the URL for a given PackageVersion
"getPackageVersionURL": utils.GetPackageVersionURL,
// 'getFindingURL' returns the URL for a given Finding
"getFindingURL": utils.GetFindingURL,
// 'add' returns the sum of two integers
"add": func(n int, incr int) int {
return n + incr
},
// 'getOtherFindingsPackageMarker' returns the key for _findingsWithNoPackages for lookup in DataMap
// Not all findings are associated with a PackageVersion, such findings are grouped under this key
// in the DataMap
"getOtherFindingsPackageMarker": func() string { return _findingsWithNoPackages },
// 'getOtherFindingsDependencyMarker' returns the key for _findingsWithNoDeps for lookup in DataMap
// Not all findings are associated with a dependency, such findings are grouped under this key
// in the DataMap
"getOtherFindingsDependencyMarker": func() string { return _findingsWithNoDeps },
// 'getFindingsCountString' returns a string with number of findings, example - "5 findings"
"getFindingsCountString": utils.GetFindingsCountString,
// 'hasFindingCategory' checks if a finding has a specific category
"hasFindingCategory": utils.HasFindingCategory,
// 'isNotEmptyString' checks if a string is not empty
"isNotEmptyString": utils.IsNotEmptyString,
// 'getCustomLocation' extracts the location from Custom field
"getCustomLocation": func(finding *endorpb.Finding) string {
return utils.GetCustomFieldValue(finding, "location")
},
// 'getCustomCodeSnippet' extracts the code snippet from Custom field
"getCustomCodeSnippet": func(finding *endorpb.Finding) string {
return utils.GetCustomFieldValue(finding, "code_snippet")
},
"fixBackticks": utils.FixUnclosedBackticks,
// 'getFirstPartyReachableFunctions' extracts first-party functions from reachable paths
"getFirstPartyReachableFunctions": utils.GetFirstPartyReachableFunctions,
// 'groupFindingsByRemediation' groups findings by their remediation value
// Returns a slice of GroupedRemediation where findings with the same remediation are grouped together
"groupFindingsByRemediation": utils.GroupFindingsByRemediation,
"consolidateRemediations": utils.ConsolidateRemediations,
}
Merge queues
If you use merge queues, Endor Labs scans the PR in the same way it would for any other PR until they are added to the merge queue. Once a PR enters the merge queue, Endor Labs does not scan the merge queue again and avoids duplicate scans and PR comments.
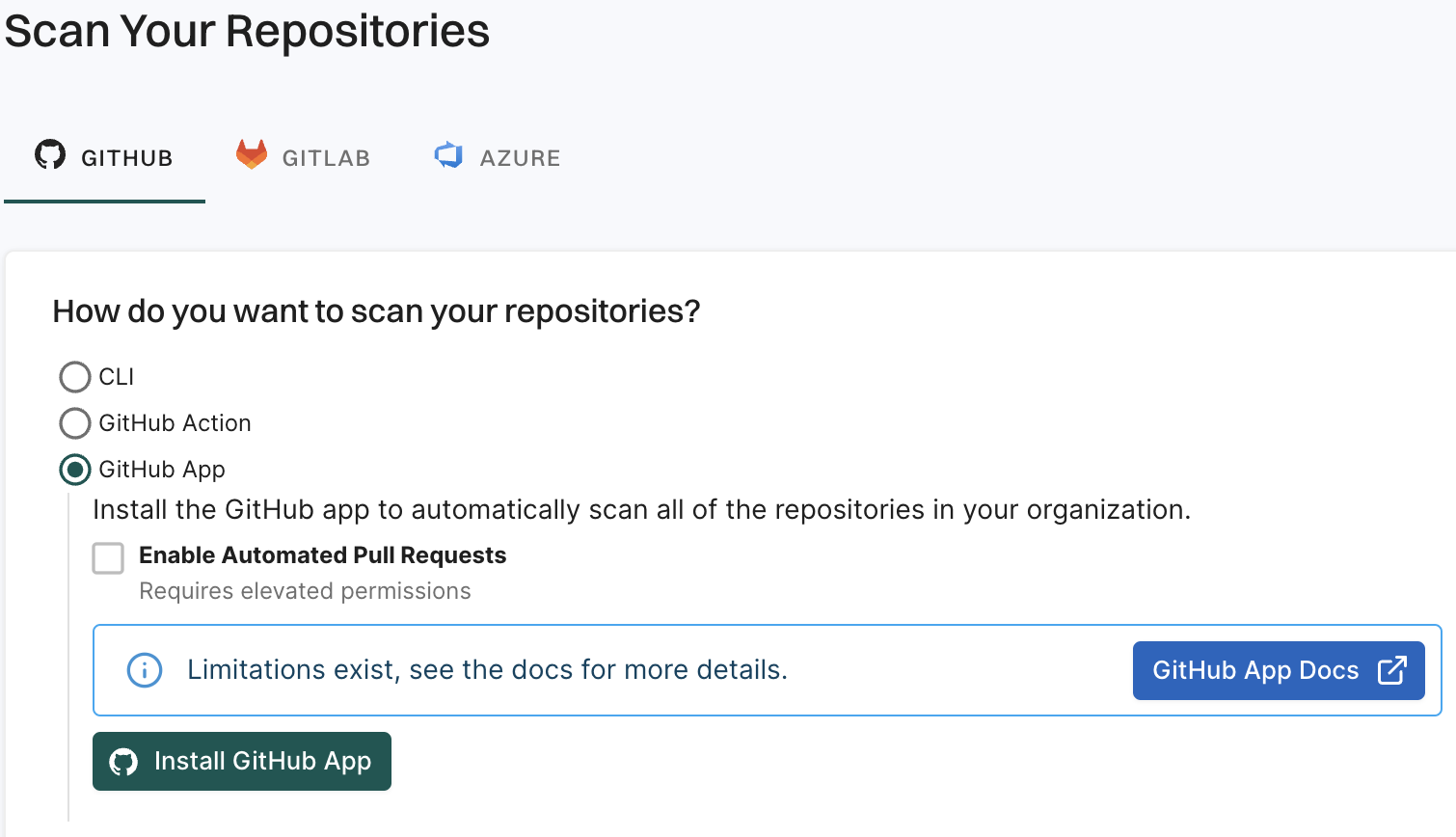
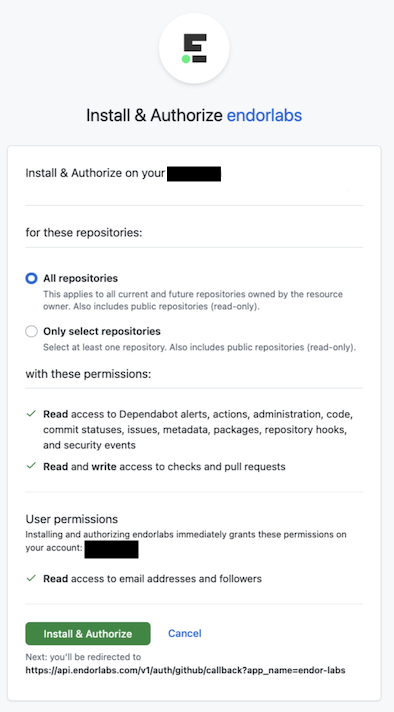




Endor Labs generates the following types of PR comments based on the nature of the findings in a scan:
FINDING_CATEGORY_SECRETS, Endor Labs adds a comment directly on the specific line where the secret is detected, using the line number provided in the finding object. These comments remain visible even if the secret is removed in a later scan.FINDING_CATEGORY_SAST, Endor Labs adds a single comment that applies to the entire PR. It summarizes all SAST-related policy violations detected during the scan. The comment is updated with each run and reflects only the latest findings.