Export scan data generated by Endor Labs to an AWS S3 storage bucket. This enables long-term data retention for compliance requirements, integration with security information and event management (SIEM) systems, and custom analytics workflows. The export framework supports exporting findings in JSON or SARIF format, allowing flexible integration with your existing toolchain.
Amazon S3 is an object storage service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It offers high durability, availability, and scalability for storing and retrieving any amount of data. S3 integrates with other AWS services and third-party tools, making it ideal for data archival, backup, and analytics workflows.
Prerequisites
Ensure that you meet the following prerequisites before exporting data to S3:
- An AWS account with permissions to create IAM roles, identity providers, and S3 buckets.
- An S3 bucket to store the exported data. See Create an S3 bucket.
- An OIDC identity provider configured to allow Endor Labs access. See Add an OIDC identity provider.
- An IAM role with permissions for Endor Labs to write to your S3 bucket. See Create an IAM role.
- Download and install endorctl. See Install endorctl.
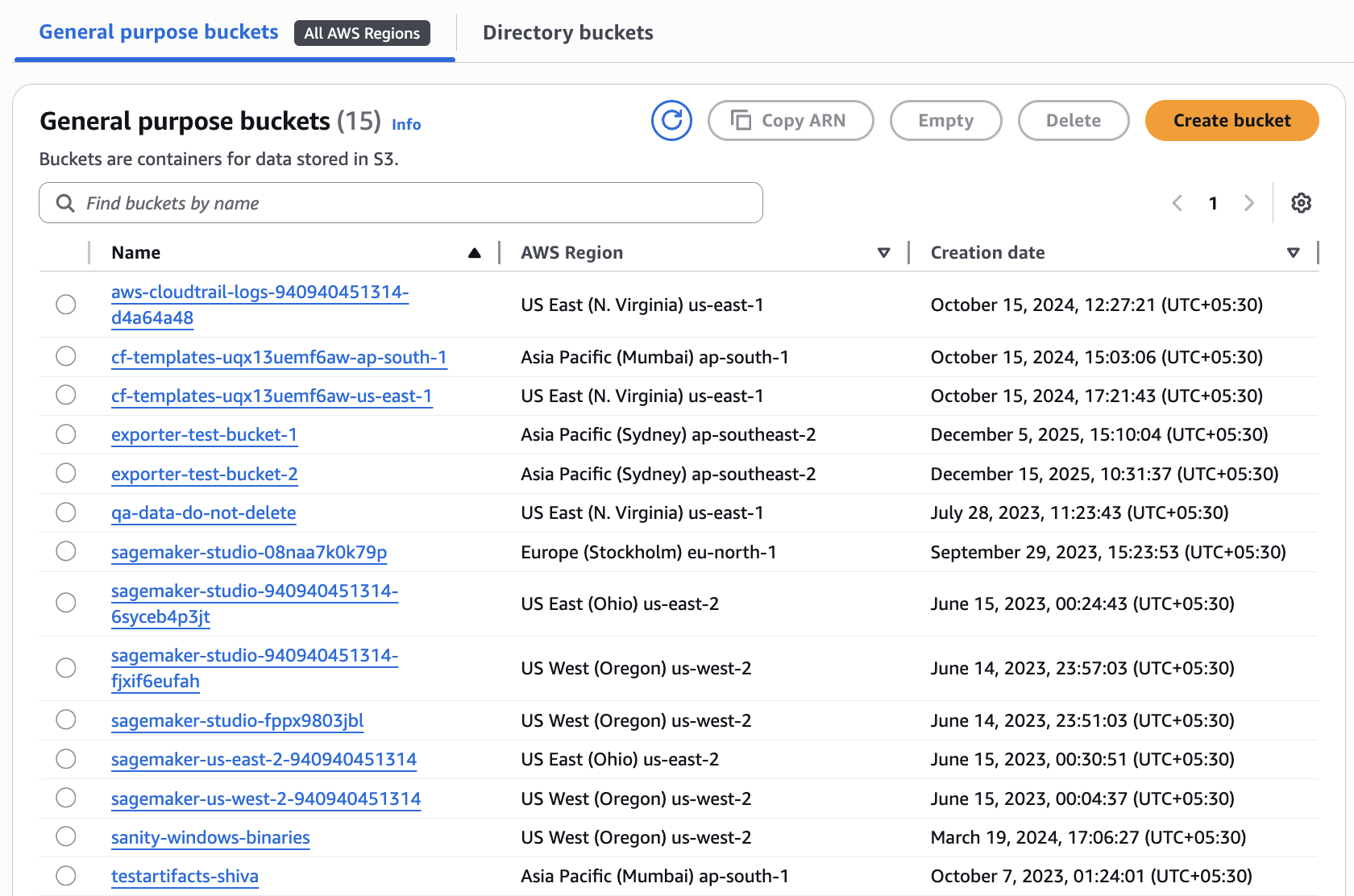
Create an S3 bucket
An S3 bucket is a container for storing objects in Amazon S3. Each bucket has a globally unique name and is created in a specific AWS region.
You can create a general purpose S3 bucket or reuse an existing bucket to store the exported data. Disable access control lists (ACLs) on the bucket to ensure that the access is managed through IAM policies and bucket policies, preventing unintended public access. Refer to Creating a bucket for detailed instructions on creating an S3 bucket.
Configure bucket lifecycle
You can configure S3 lifecycle rules to automatically delete exported data after a specified retention period. Exported objects do not expire unless you configure lifecycle rules.
- In the AWS management console, navigate to Amazon S3 > Buckets.
- Select your bucket.
- Select Management and click Create lifecycle rule.
- Enter a Lifecycle rule name, for example,
endor-exports-expiry. - Under Filter type, select Limit the scope of this rule using one or more filters and enter
endor/as the prefix to apply the rule only to exported data. - Under Lifecycle rule actions, select Expire current versions of objects.
- Under Expire current versions of objects, enter the number of days after which objects should be deleted.
- Review the rule and click Create rule.
Configure access for Endor Labs
Endor Labs uses OIDC federation to assume an IAM role in your AWS account to access the S3 bucket. To allow Endor Labs to write to the bucket, configure OIDC and IAM using one of the following methods:
- Use the CFT template to create the OIDC identity provider, IAM role, and S3 write policy.
- Use the AWS Management console to create access by adding the OIDC identity provider and IAM role.
Create AWS resources using a CFT template
Use an AWS CloudFormation Template (CFT) to create the IAM role and S3 PutObject policy for the S3 exporter. The template can create a new OIDC identity provider for Endor Labs or reuse an existing provider in your account.
The following table lists the parameters you can set when deploying the CFT template.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
OIDCUrl |
Endor Labs OIDC issuer URL. |
ExistingOidcProviderArn |
Set this to the ARN of your existing OIDC provider for api.endorlabs.com. The template will reuse it and will not create a new OIDC provider. |
OidcAudience |
Audience for the OIDC trust policy. Use the same value for allowed_audience when creating the S3 exporter. |
TenantNamespace |
Your Endor Labs tenant namespace. |
BucketName |
Name of the existing S3 bucket that will receive exports. |
RoleName |
IAM role name that Endor Labs will assume via web identity. |
PolicyName |
IAM managed policy name for S3 PutObject permission. |
-
Create a
.cftfile with the following template.You can use the following template and set the parameters according to your OIDC audience, tenant namespace, bucket name, role name, and optionally an existing OIDC provider ARN.
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: "2010-09-09" Description: > Endor Labs S3 Exporter - creates IAM OIDC provider (optional), role, and minimal S3 PutObject policy. Parameters: OIDCUrl: Type: String Default: "https://api.endorlabs.com" Description: "Endor Labs OIDC issuer URL." ExistingOidcProviderArn: Type: String Default: "" Description: > Optional. If your AWS account already has an OIDC provider for https://api.endorlabs.com, set this to its ARN (for example, arn:aws:iam::<ACCOUNT_ID>:oidc-provider/api.endorlabs.com). When set, this template will NOT create a new OIDC provider. It will reuse the existing provider and ensure the OidcAudience is present in its ClientIdList. OidcAudience: Type: String Default: "s3-exporter" Description: "Specify the audience name to use in the OIDC trust policy. Set the same value in allowed_audience while creating the Endor exporter configuration." TenantNamespace: Type: String Description: "Root Endor Labs tenant namespace (for example, acme-corp)." BucketName: Type: String Description: "Existing S3 bucket name to receive exports." RoleName: Type: String Default: "EndorS3ExporterRole" Description: "IAM role name Endor will assume via web identity." PolicyName: Type: String Default: "EndorS3ExporterPolicy" Description: "IAM managed policy name for S3 PutObject permission." Conditions: CreateOidcProvider: !Equals [!Ref ExistingOidcProviderArn, ""] UseExistingOidcProvider: !Not [!Equals [!Ref ExistingOidcProviderArn, ""]] Resources: EndorOidcProvider: Type: AWS::IAM::OIDCProvider DeletionPolicy: Delete UpdateReplacePolicy: Delete Condition: CreateOidcProvider Properties: Url: !Ref OIDCUrl ClientIdList: - !Ref OidcAudience EndorS3PutObjectPolicy: Type: AWS::IAM::ManagedPolicy DeletionPolicy: Delete UpdateReplacePolicy: Delete Properties: ManagedPolicyName: !Ref PolicyName PolicyDocument: Version: "2012-10-17" Statement: - Sid: PutObjectToBucket Effect: Allow Action: - s3:PutObject Resource: !Sub "arn:${AWS::Partition}:s3:::${BucketName}/*" EndorS3ExporterRole: Type: AWS::IAM::Role DeletionPolicy: Delete UpdateReplacePolicy: Delete Properties: RoleName: !Ref RoleName AssumeRolePolicyDocument: Version: "2012-10-17" Statement: - Sid: EndorWebIdentity Effect: Allow Principal: Federated: !If - CreateOidcProvider - !Ref EndorOidcProvider - !Ref ExistingOidcProviderArn Action: sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity Condition: StringEquals: "api.endorlabs.com:aud": !Ref OidcAudience StringLike: "api.endorlabs.com:sub": - !Sub "${TenantNamespace}/*" - !Sub "${TenantNamespace}.*/*" ManagedPolicyArns: - !Ref EndorS3PutObjectPolicy Outputs: OidcProviderArn: Description: "OIDC provider ARN." Value: !If - CreateOidcProvider - !Ref EndorOidcProvider - !Ref ExistingOidcProviderArn RoleArn: Description: "Role ARN to set as assume_role_arn in Endor exporter config." Value: !GetAtt EndorS3ExporterRole.Arn OidcAudienceOut: Description: "Audience to set as allowed_audience in Endor exporter config." Value: !Ref OidcAudience -
Save this file with an appropriate name such as
endorlabs-s3-export.cft. -
Sign into AWS CloudFormation and search for Stacks.
-
Click Create Stack and select With new resources.
-
From Template source, select Upload a template file.
-
Click Choose file, select the file you saved, and click Next.
-
In Specify stack details, enter a Stack name, verify the Parameters you entered in the script and click Next.
-
Select the acknowledgement from Configure stack options and click Next.
-
From Review and Create, review the details and click Submit.
Check the progress of the creation of your resources from Stacks. Once the stack is created, you can see the status as CREATE_COMPLETE.
Create access through the Console
Create the OIDC identity provider and IAM role manually in the AWS Management Console.
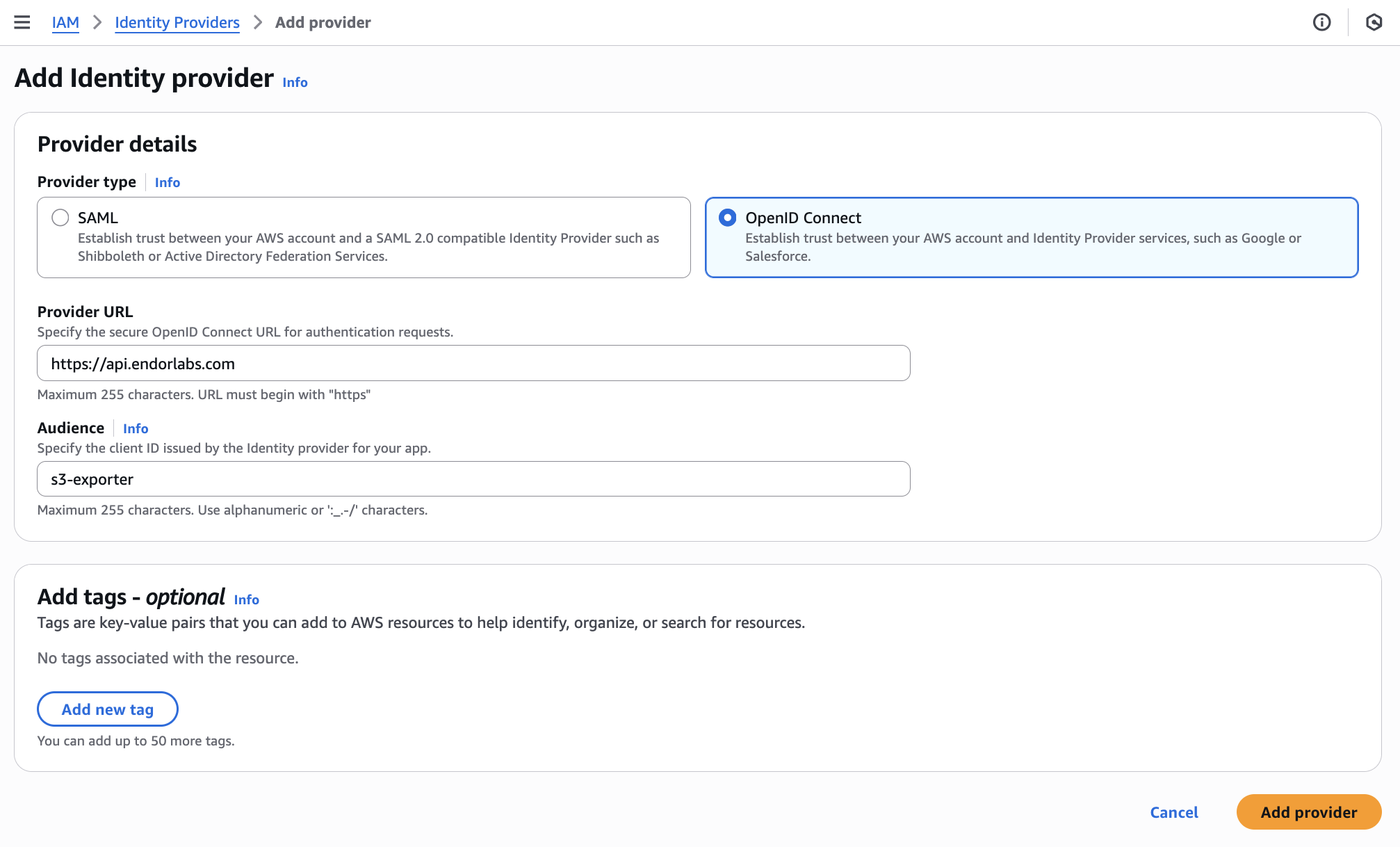
1. Add an OIDC identity provider
OpenID Connect (OIDC) federation allows Endor Labs to access AWS resources without requiring long-lived credentials. This reduces the risk of credential exposure and simplifies secret rotation.
- In the AWS management console, navigate to IAM > Access Management > Identity providers.
- Click Add provider.
- Under Provider details, select OpenID Connect.
- For Provider URL, enter
https://api.endorlabs.com. - For Audience, specify a unique identifier to validate incoming OIDC tokens from Endor Labs.
- Optionally, add tags to help identify the provider.
- Click Add provider.
2. Create an IAM role
Create an IAM role that Endor Labs can assume to write to your S3 bucket. This involves:
- Create a permissions policy: Define the S3 write permissions.
- Create an IAM role: Create a role with OIDC trust and attach the policy.
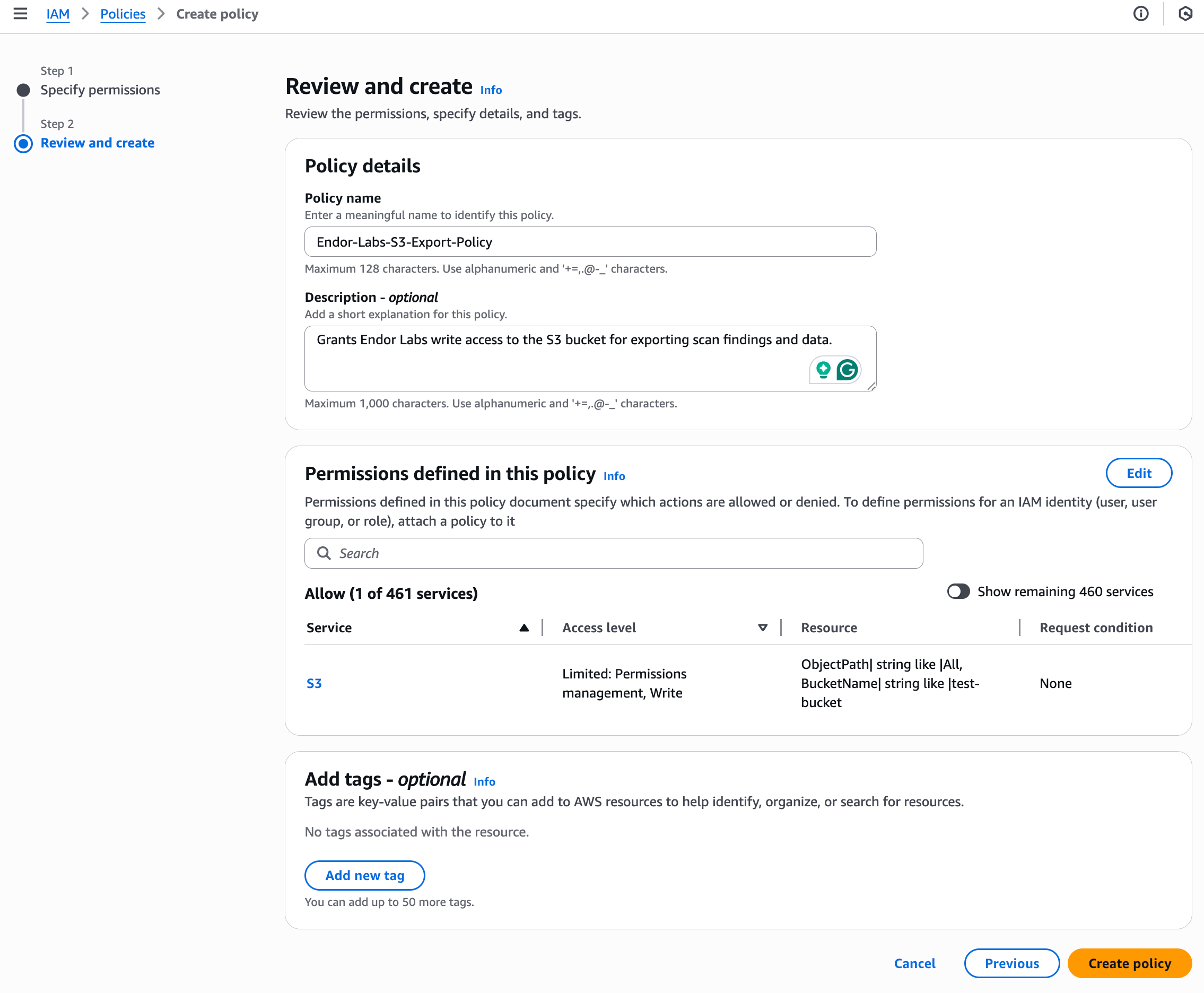
Create a permissions policy
-
In the AWS management console, navigate to IAM > Access Management > Policies.
-
Click Create policy.
-
Under Specify permissions, toggle the Policy editor to JSON.
-
Enter the following policy:
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "s3:PutObject" ], "Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::<your-bucket-name>/*" } ] }Replace
<your-bucket-name>with the name of your S3 bucket. -
Click Next.
-
Under Review and create, enter a Policy name. For example,
EndorLabsS3ExportPolicy. -
Review the Permissions defined in this policy section to confirm that the expected Amazon S3 write actions are included.
-
Optionally, add a description and tags to your policy.
-
Click Create policy.
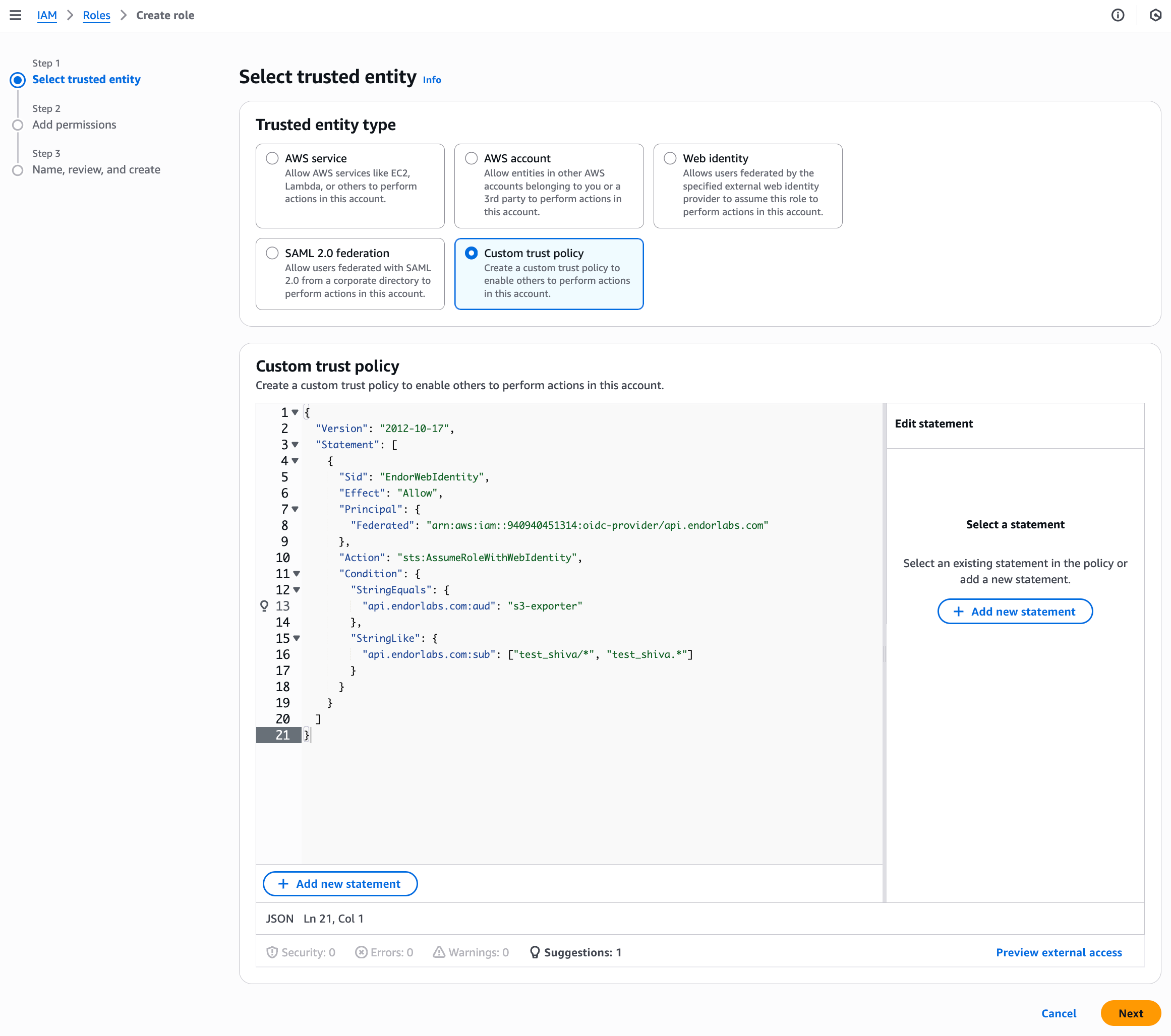
Create an IAM role
- In the AWS management console, navigate to IAM > Access Management > Roles.
- Click Create role.
- Under Select trusted entity, select Custom trust policy.
- Enter the following trust policy:
Replace the placeholders with your values:
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Sid": "EndorWebIdentity", "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "Federated": "arn:aws:iam::<aws-account-id>:oidc-provider/api.endorlabs.com" }, "Action": "sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity", "Condition": { "StringEquals": { "api.endorlabs.com:aud": "<oidc-audience>" }, "StringLike": { "api.endorlabs.com:sub": [ "<your-namespace>/*", "<your-namespace>.*" ] } } } ] }<aws-account-id>: Your AWS account ID<oidc-audience>: The audience value you configured in the OIDC provider<your-namespace>: Your Endor Labs namespace
- Click Next.
- Under Add permissions, search for and select the IAM policy you created.
- Click Next.
- Under Name, review, and create, enter a Role name for the S3 exporter role. For example,
EndorLabsS3ExporterRole.
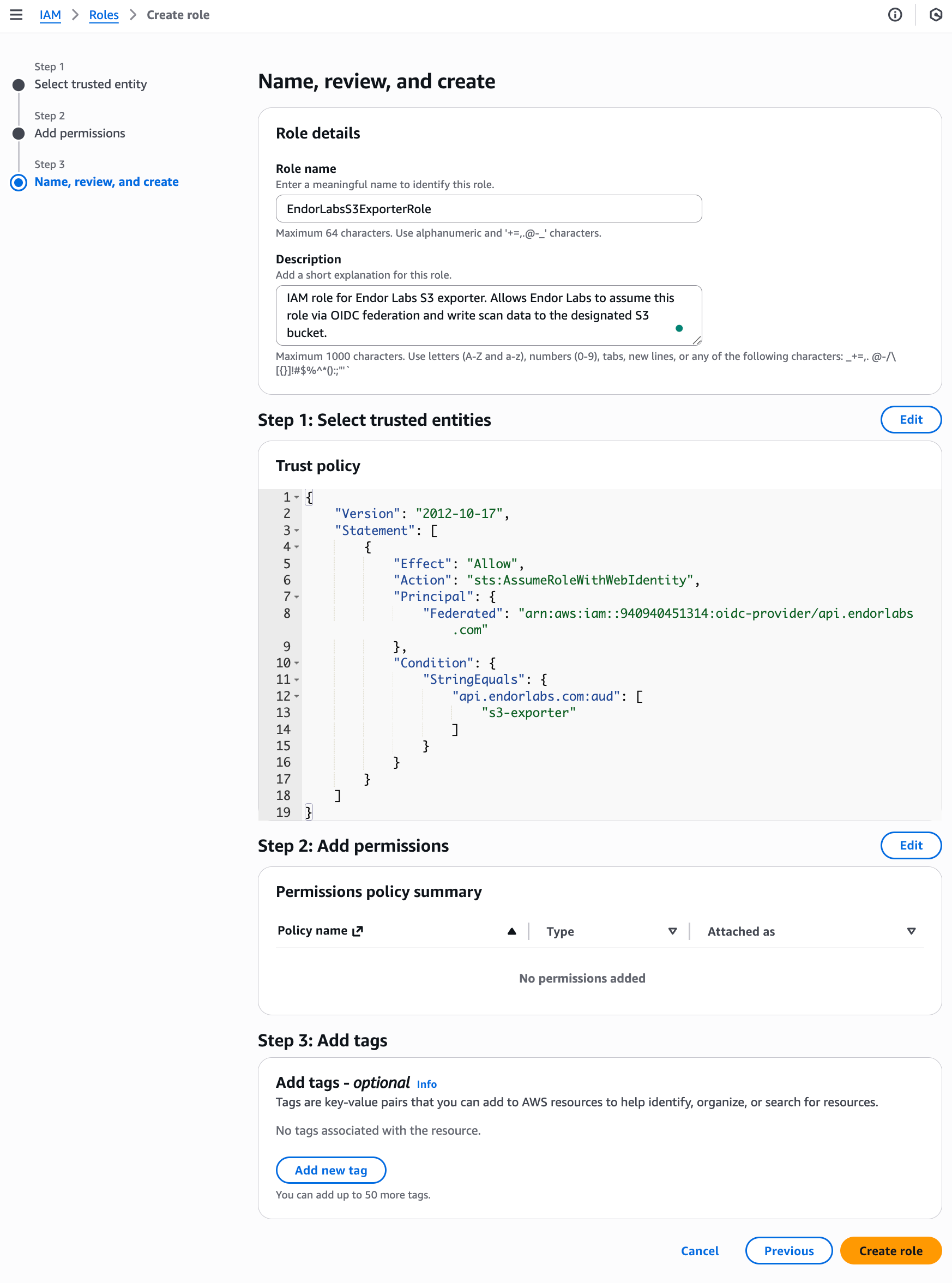
- Optionally, add tags to help identify the role.
- Click Create role.
Create an S3 exporter
Create an S3 exporter using the Endor Labs API to configure the export destination and data types.
The following table lists the configuration options required to create the exporter.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
<namespace> |
Your Endor Labs namespace |
<exporter-name> |
A descriptive name for the exporter |
<your-bucket-name> |
The name of your S3 bucket |
<aws-region> |
The AWS region where your bucket is located, for example us-east-1. Refer to AWS regions for a list of region codes. |
<iam-role-arn> |
The ARN of the IAM role you created |
<oidc-audience> |
The audience value that you configured in the OIDC provider |
Run the following command to create an S3 exporter.
endorctl api create \
--namespace=<namespace> \
--resource=Exporter \
--data '{
"meta": {
"name": "<exporter-name>"
},
"propagate": true,
"spec": {
"exporter_type": "EXPORTER_TYPE_S3",
"s3_config": {
"bucket_name": "<your-bucket-name>",
"region": "<aws-region>",
"assume_role_arn": "<iam-role-arn>",
"allowed_audience": "<oidc-audience>"
},
"message_type_configs": [
{
"message_type": "MESSAGE_TYPE_FINDING",
"message_export_format": "MESSAGE_EXPORT_FORMAT_JSON"
}
]
}
}'
For example, to create an S3 exporter named s3-findings-exporter in the namespace doe.deer that exports findings in JSON format, run the following command.
endorctl api create \
--namespace=doe.deer \
--resource=Exporter \
--data '{
"meta": {
"name": "s3-findings-exporter"
},
"propagate": true,
"spec": {
"exporter_type": "EXPORTER_TYPE_S3",
"s3_config": {
"bucket_name": "my-endorlabs-exports",
"region": "us-west-2",
"assume_role_arn": "arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/EndorLabsS3ExportRole",
"allowed_audience": "s3-exporter"
},
"message_type_configs": [
{
"message_type": "MESSAGE_TYPE_FINDING",
"message_export_format": "MESSAGE_EXPORT_FORMAT_JSON"
}
]
}
}'
Configure scan profile to use the S3 exporter
After creating the exporter, associate it with your scan profile. You can also set the scan profile as the default for your namespace so all projects use it automatically. See Scan profiles for more information.
Configure the scan profile
- Select Settings from the left sidebar.
- Select Scan Profiles.
- Select the scan profile you want to configure and click Edit Scan Profile.
- Select your exporter under Exporters and click Save Scan Profile.
Configure the project to use the scan profile
Associate your project with a scan profile to enable automatic export of scan data.
- Select Projects from the left sidebar and select the project you want to configure.
- Select Settings and select the scan profile you want to use under Scan Profile.
Scan projects to export data
After configuration, subsequent scans automatically export data to your S3 bucket. You can trigger a scan immediately using the rescan feature. See Rescan projects for more information.
To validate that the S3 exporter ran successfully for a scan:
-
Select Projects from the left sidebar and select the project associated with your exporter.
-
Select Scan History and select a record to view its information.
-
Select Logs to view the scan log and set the log level to All
The following message confirms that the S3 export is successful.
INFO: Successfully completed S3 export
Exported file structure
Endor Labs exports data to S3 using a hierarchical folder structure:
endor/
└── <exporter-uuid>-<exporter-name>/
└── <namespace>/
└── <project-uuid>-<project-name>/
└── <scan-type>/
└── <ref-or-pr>/
└── <timestamp>_<scan-uuid>.zip
Each path segment is defined as follows:
| Level | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Root | endor/ |
Fixed prefix for all Endor exports |
| Exporter | abc123-prod-exporter/ |
<exporter_uuid>-<exporter_name> - unique per exporter |
| Namespace | acme-corp/ |
Your Endor Labs namespace |
| Project | def456-my-service/ |
<project-uuid>-<project-name> |
| Scan Type | schedule/ or pr/ |
Type of scan that triggered export |
| Ref or PR Number | <branch-name>/ or <pr-id> |
Name of the branch or PR number |
| File | 20251215T143025Z_xyz789.zip |
<timestamp>_<scan-uuid>.zip |
Example file path
my-bucket/endor/abc123-prod-exporter/acme-corp/6efgh-pythonrepo/schedule/main/20251215T143025Z_xyz789.zip
Manage the S3 exporter
You can list, update, and delete S3 exporters using the Endor Labs API.
List exporters
Run the following command to list all exporters in your namespace.
endorctl api list --namespace=<namespace> --resource=Exporter
Update an exporter
Run the following command to update an existing exporter. Use the --field-mask parameter to specify the fields to update.
endorctl api update \
--namespace=<namespace> \
--resource=Exporter \
--name=<exporter-name> \
--field-mask "spec.s3_config.region" \
--data '{
"spec": {
"s3_config": {
"region": "us-west-2"
}
}
}'
Delete an exporter
Run the following command to delete an exporter.
endorctl api delete --namespace=<namespace> --resource=Exporter --name=<exporter-name>